A technical documentation page is a web page that provides technical information about a product or process.
It is typically written for technical users, such as developers, engineers, or IT professionals.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to style the header, sidebar menu, and main content of our documentation page.
Prerequisites
To understand this tutorial, you should have a basic understanding of HTML and CSS. If you are not familiar with HTML and CSS, read our comprehensive HTML Tutorial and CSS Tutorial.
CSS concepts to design our technical documentation page:
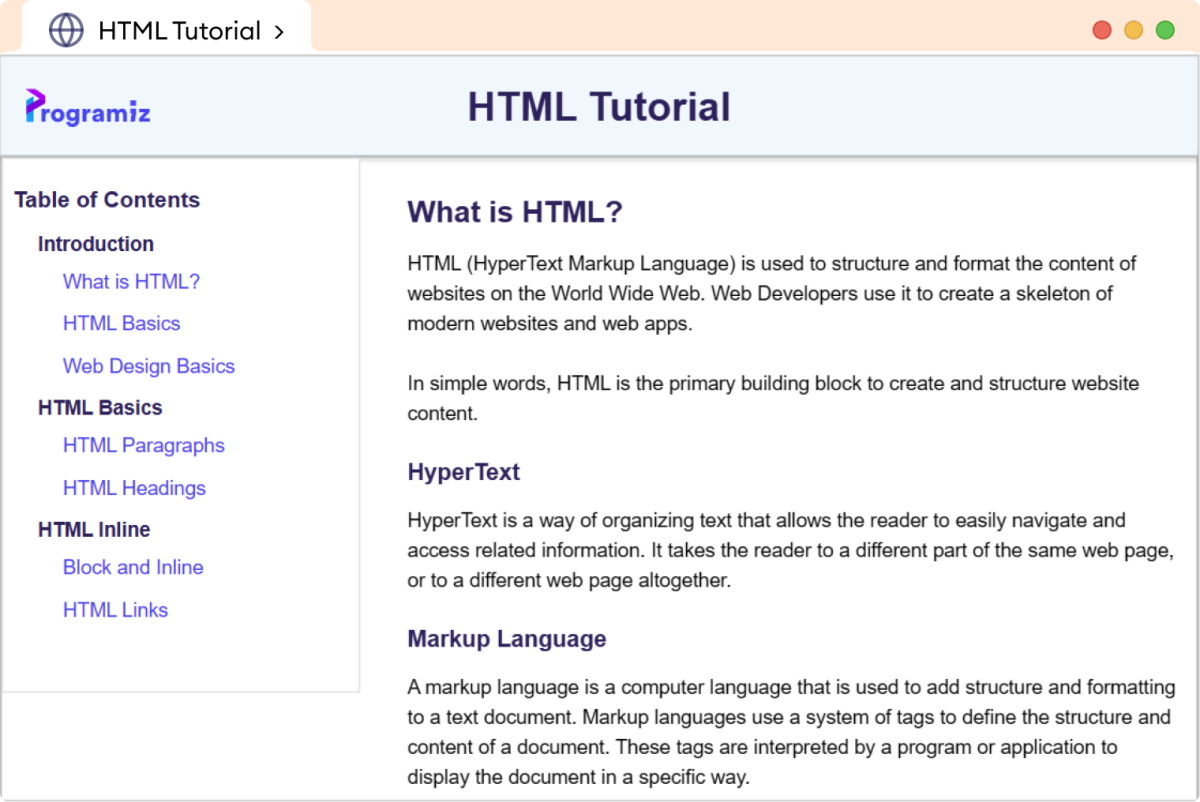
Layout of HTML Documentation Page
The final layout of our HTML documentation page will look like this:
Approach
To develop our technical documentation, we will have the following steps:
1. First, create a header having our logo and main heading.
2. Create a sidebar with a table of contents.
3. Create a main section with all content.
4. Finally, add a footer to our technical documentation page.
Let's start building our page.
Resetting Browser Stylesheet Rule
Before we jump to build our technical documentation page, let's reset the browser's default stylesheet in our CSS to gain greater control over the layout.
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}Resetting the browser's padding and margins to 0 ensures precise control over the width and height of elements.
Additionally, setting the box-sizing property to border-box allows both padding and border to be added within the width and height of the element.
Step 1: Create a Header
In the first step, let's create a header containing a logo and a main heading.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>HTML Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- header element consisting of a logo and a heading -->
<header>
<div class="logo-wrapper">
<img
src="https://cdn.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/pc_logo.svg"
alt="Programiz Logo"
/>
</div>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
</header>
</body>
</html>/* resets the browser default spacing */
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
width: 100%;
max-width: 760px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* styles the header element */
header {
height: 80px;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 4px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.116);
background-color: aliceblue;
}
/* styles for logo wrapper*/
header .logo-wrapper {
width: 100px;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 20px;
transform: translateY(-50%);
cursor: pointer;
}
/* styles to fit logo image within the logo wrapper */
.logo-wrapper img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
object-fit: cover;
}
/* style for the main heading of page */
header h1 {
line-height: 80px;
color: #25265e;
}Browser Output

HTML Tutorial
Here,
- Setting
position: relativein the header allows the.logo-wrapper(child element) to be positioned relative to it. Otherwise, it would be positioned relative to the document, i.e., the body element.
- Using
position: absolutemoves the.logo-wrapperout of the header flow and allows for precise positioning within the header.
- The value of
top: 50%positions the logo from50%of the height of the header, andleft: 20pxmoves the logo20pxfrom the left of the document.
- Setting
line-height: 80pxfor theh1element makes its line height equal to the height of the header, which centers the text vertically within the header.
Step 2: Create a sidebar
Now, let's add a sidebar with a table of content for our page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>HTML Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- header is here -->
<main class="main">
<!-- a sidebar consisting of menu of documentation page -->
<aside class="table-of-content">
<h2 class="menu-heading">Table of Contents</h2>
<!-- main menu of table of content -->
<ul class="main-menu">
<li class="menu-sub-heading">Introduction</li>
<!-- submenu -->
<ul class="sub-menu">
<li><a href="#what-is-html">What is HTML?</a></li>
<li><a href="#html-basics">HTML Basics</a></li>
<li>
<a href="#web-design-basics">Web Design Basics</a>
</li>
</ul>
<li class="menu-sub-heading">HTML Basics</li>
<!-- submenu -->
<ul class="sub-menu">
<li>
<a href="#html-paragraphs">HTML Paragraphs</a>
</li>
<li><a href="#html-headings">HTML Headings</a></li>
</ul>
<li class="menu-sub-heading">HTML Inline</li>
<!-- submenu -->
<ul class="sub-menu">
<li>
<a href="#block-and-inline">Block and Inline</a>
</li>
<li><a href="#html-links">HTML Links</a></li>
</ul>
</ul>
</aside>
<!-- main content of documentation page will be here -->
</main>
<!-- footer will be here -->
</body>
</html>.table-of-content {
/* remaining width for the main content of page */
width: 30%;
height: 450px;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.137);
color: #25265e;
padding: 8px;
/* makes the sidebar sticky */
position: sticky;
top: 0px;
}
.menu-heading {
margin-bottom: 20px;
font-size: 18px;
}
.table-of-content ul {
/* removes the bullet points in list items */
list-style-type: none;
/* list item marker is placed within the content area of the list item */
list-style-position: inside;
padding-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
/* styles for sub-heading inside our menu */
.menu-sub-heading {
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: none;
margin-bottom: 12px;
color: #25265e;
}
/* provides the bottom spacing for each list item in menu */
.sub-menu li {
margin-bottom: 16px;
}
/* color the menu item */
.table-of-content a {
color: #0556f3;
text-decoration: none;
}
/* change color of menu items while hovering */
.table-of-content a:hover {
color: #03338f;
}Browser Output

HTML Tutorial
Table of Contents
In the above step,
- Setting
width: 30%allows the sidebar to occupy30%width of the viewport or device.
- Using
position: stickymakes the sidebar sticky at the top (0px) of the page, making it easier to navigate the entire content.
- Pseudo-class selector
a:hoverstyles links based on being hovered.
Step 3: Add a Main Section
In this step, we will add all the content to our technical documentation page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>HTML Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- header is here -->
<main class="main">
<!-- a sidebar consisting of menu of documentation page -->
<!-- main content of the documentation page -->
<section class="main-content">
<h2 id="what-is-html">What is HTML?</h2>
<p>
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is used to structure and
format the content of websites on the World Wide Web. Web
Developers use it to create a skeleton of modern websites
and web apps.
</p>
<p>
In simple words, HTML is the primary building block to
create and structure website content.
</p>
<h3>HyperText</h3>
<p>
HyperText is a way of organizing text that allows the reader
to easily navigate and access related information. It takes
the reader to a different part of the same web page, or to a
different web page altogether.
</p>
<h3>Markup Language</h3>
<p>
A markup language is a computer language that is used to add
structure and formatting to a text document. Markup
languages use a system of tags to define the structure and
content of a document. These tags are interpreted by a
program or application to display the document in a specific
way.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2>Example of HTML</h2>
<p>Let's see a simple example of HTML.</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>programiz</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
<p>You'll learn about HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-example-on-browser.png"
alt="Browser Output"
/>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-basics">HTML Basics</h2>
<p>
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used
to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses
various tags to define the different elements on a page,
such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
</p>
<h3>HTML Hierarchy</h3>
<p>
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be
nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of
the content on the web page.
</p>
<p>
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document
Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render
the web page. For example,
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page. </p>
<p>
It contains a <strong>main heading </strong> and
<em> paragraph </em>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-basics-hierarchy.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<p>
In this example, the html element is the root element of the
hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body.
The head element, in turn, contains a child element called
the title, and the body element contains child elements: h1
and p.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="web-design-basics">Web Design Basics</h2>
<p>
Web design refers to the process of creating and styling the
appearance of a website. There are 3 fundamental
technologies to build the modern website and web
applications. They are:
</p>
<ul>
<li>HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>JS</li>
</ul>
<p>
These technologies work together to provide the structure,
style, and interactivity of a web page.
</p>
<h3>HTML</h3>
<p>
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used
to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses
various tags to define the different elements on a page,
such as headings, paragraphs, and links. Let's see an
example:
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorials.</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/web-design-basics-html-example.png"
alt="HTML example"
/>
<p>Here, we have an HTML document where:</p>
<ul>
<li>
<span><h1></span>— heading of the document
</li>
<li>
<span><p></span>—paragraph of the document
</li>
</ul>
<p>
The heading and paragraph tag in the above code help create
a webpage structure.
</p>
<h3>CSS</h3>
<p>
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language. It is
used to style HTML documents.
</p>
<p>
It specifies how the elements of HTML look including their
layout, colors, and fonts. We use <style> tag to add
CSS to HTML documents. Let's add some CSS to our previous
HTML code.
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorial.</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/web-design-basics-css-example.png"
alt="HTML example"
/>
<p>
In the above code, we've applied CSS to <h1> and
<p> tags to change their text color. Notice the code,
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
</code>
</pre>
<p>
This CSS code turns the text color of every <h1>
element into blue.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-paragraphs">HTML Paragraphs</h2>
<p>The HTML tag is used to create paragraphs. For example,</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code><p>HTML is fun to learn.</p></code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-paragraph.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<p>
As we can see, a paragraph starts with the <p> and
ends with the </p> tag.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-headings">HTML Headings</h2>
<p>
The HTML heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) are used to
add headings to a webpage. For example,
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<h1>This is heading 1.</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2.</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3.</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4.</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5.</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6.</h6>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/headings-in-html.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<p>
In the example, we have used tags h1 to h6 to create
headings of varying sizes and importance.
</p>
<p>
The h1 tag denotes the most important heading on a webpage.
Similarly, h6 denotes the least important heading.
</p>
<p>
The difference in sizes of heading tags comes from the
browser's default styling. And, you can always change the
styling of heading tags, including font size, using CSS.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="block-and-inline">HTML Inline and Block Elements</h2>
<p>
HTML elements can be broadly categorized into one of two
categories:
</p>
<ul>
<li>
Inline Elements: <span>, <a>,
<strong>, <img> etc.
</li>
<li>
Block Elements: <p>, <div>, <h1>,
<figure> etc.
</li>
</ul>
<h3>HTML Inline Elements</h3>
<p>
Inline elements are displayed on the same line. They do not
start on a new line and take up only as much width as their
contents require. An example of an inline element is the
<span> tag.
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<p>This is how <span style="border: 1px solid black">span</span> works. </p>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-inline-example.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-links">HTML Links</h2>
<p>
HTML links or hyperlinks connect one resource on the web to
another. The resource may be an image, a web page, a
program, a video clip, an audio clip, an element within a
web page, etc, or anything that can be hosted on the
internet.
</p>
<p>
We use the HTML <a> tag to create hyperlinks. The
syntax for the <a> tag is
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<a href="URL"> Text </a>
</code>
</pre>
<p>Here,</p>
<ul>
<li>URL - the destination of the link</li>
<li>Text - the part that will be visible as a link</li>
</ul>
<p>
Clicking on the text will navigate you to the resource in
the URL. For example,
</p>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-link-example.png"
alt="HTML example"
/>
<p>
Here, clicking on the Swift Continue Statement will take you
to
</p>
<p>
<a
href="https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement"
>https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement.</a
>
</p>
</section>
<!-- main content of documentation page will be here -->
</main>
<!-- footer will be here -->
</body>
</html>.main {
/* default width is always 100% */
width: 100%;
/* aligns the sidebar and main content horizontally next to each other */
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
/* adds 20px space between sidebar and main content */
gap: 20px;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 4px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.116);
position: relative;
}
/* styes for the main content */
.main-content {
/* sets 70% width of the document, 25% is occupied by sidebar earlier,
and remaining for spacing between them */
width: 70%;
padding: 10px;
margin-left: auto;
}
h2,
h3 {
color: #25265e;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 24px;
line-height: 24px;
}
/* styles the under ordered list in main element */
.main ul {
list-style-position: inside;
padding-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
/* adds a margin to top and bottom for hr element for spacing */
.section-break {
margin: 24px 0px;
}
/* styles the code block */
pre.code-block {
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.13);
background-color: aliceblue;
margin-bottom: 24px;
white-space: pre-line;
}
/* images are allowed to shrink for smaller screen sizes */
.main-content img {
max-width: 100%;
}Browser Output

HTML Tutorial
Table of Contents
What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is used to structure and format the content of websites on the World Wide Web. Web Developers use it to create a skeleton of modern websites and web apps.
In simple words, HTML is the primary building block to create and structure website content.
HyperText
HyperText is a way of organizing text that allows the reader to easily navigate and access related information. It takes the reader to a different part of the same web page, or to a different web page altogether.
Markup Language
A markup language is a computer language that is used to add structure and formatting to a text document. Markup languages use a system of tags to define the structure and content of a document. These tags are interpreted by a program or application to display the document in a specific way.
Example of HTML
Let's see a simple example of HTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>programiz</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
<p>You'll learn about HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

HTML Basics
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
HTML Hierarchy
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of the content on the web page.
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render the web page. For example,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page. </p>
<p>
It contains a <strong>main heading </strong> and
<em> paragraph </em>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In this example, the html element is the root element of the hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body. The head element, in turn, contains a child element called the title, and the body element contains child elements: h1 and p.
Web Design Basics
Web design refers to the process of creating and styling the appearance of a website. There are 3 fundamental technologies to build the modern website and web applications. They are:
- HTML
- CSS
- JS
These technologies work together to provide the structure, style, and interactivity of a web page.
HTML
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links. Let's see an example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorials.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

Here, we have an HTML document where:
- <h1>— heading of the document
- <p>—paragraph of the document
The heading and paragraph tag in the above code help create a webpage structure.
CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language. It is used to style HTML documents.
It specifies how the elements of HTML look including their layout, colors, and fonts. We use <style> tag to add CSS to HTML documents. Let's add some CSS to our previous HTML code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorial.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In the above code, we've applied CSS to <h1> and <p> tags to change their text color. Notice the code,
h1 {
color: blue;
}
This CSS code turns the text color of every <h1> element into blue.
HTML Paragraphs
The HTML tag is used to create paragraphs. For example,
<p>HTML is fun to learn.</p>
Browser Output

As we can see, a paragraph starts with the <p> and ends with the </p> tag.
HTML Headings
The HTML heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) are used to add headings to a webpage. For example,
<h1>This is heading 1.</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2.</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3.</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4.</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5.</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6.</h6>
Browser Output

In the example, we have used tags h1 to h6 to create headings of varying sizes and importance.
The h1 tag denotes the most important heading on a webpage. Similarly, h6 denotes the least important heading.
The difference in sizes of heading tags comes from the browser's default styling. And, you can always change the styling of heading tags, including font size, using CSS.
HTML Inline and Block Elements
HTML elements can be broadly categorized into one of two categories:
- Inline Elements: <span>, <a>, <strong>, <img> etc.
- Block Elements: <p>, <div>, <h1>, <figure> etc.
HTML Inline Elements
Inline elements are displayed on the same line. They do not start on a new line and take up only as much width as their contents require. An example of an inline element is the <span> tag.
<p>This is how <span style="border: 1px solid black">span</span> works. </p>
Browser Output

HTML Links
HTML links or hyperlinks connect one resource on the web to another. The resource may be an image, a web page, a program, a video clip, an audio clip, an element within a web page, etc, or anything that can be hosted on the internet.
We use the HTML <a> tag to create hyperlinks. The syntax for the <a> tag is
<a href="URL"> Text </a>
Here,
- URL - the destination of the link
- Text - the part that will be visible as a link
Clicking on the text will navigate you to the resource in the URL. For example,
Browser Output

Here, clicking on the Swift Continue Statement will take you to
https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement.
In the above step,
- Setting
display: flexfor the<main>element allows its immediate child elements (sidebarandmain-contentsection) to be aligned horizontally next to each other.
- Setting
width: 70%on the.main-contentelement allows the document information to occupy70%of the available width, while the sidebar, which was previously assigned30%, takes up the remaining space.
- Setting the
white-spaceproperty topre-linefor thepretag eliminates the line spacing within a single line.
- Setting
max-width: 100%on images means images will never be wider than its parent container.
Step 4: Adding a footer
In this step, we will add a footer to our page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>HTML Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- header goes in here -->
<!-- main element wrapping the sidebar menu and content -->
<!-- Adding a footer -->
<footer>
<p>HTML Documentation Page © Programiz, 2023</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>/* reset browsers style */
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/* style for footer */
footer {
height: 50px;
font-size: 14px;
text-align: center;
color: #25265e;
background-color: aliceblue;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 4px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.116);
}
/* provide line-height same as height of footer to vertically center */
footer p {
line-height: 50px;
}Browser Output

HTML Tutorial
HTML Documentation Page © Programiz, 2023
Here,
- Setting the footer's
heightto50pxand applying the sameline-heightto its child paragraph element allows the content to be vertically centered.
- Setting the
text-alignproperty tocenteraligns the content horizontally in the middle.
Step 5: Optimize Page for Mobile Devices
Finally, let's add media queries to make our HTML Documentation Page responsive for mobile devices.
@media screen and (max-width: 672px) {
/* the sidebar and content are stacked on top of each other */
.main {
flex-direction: column;
}
/* takes the full width of the document */
.table-of-content {
width: 100%;
position: relative;
}
/* takes the full width of document */
.main-content {
width: 100%;
}
}Browser Output

HTML Tutorial
Table of Contents
What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is used to structure and format the content of websites on the World Wide Web. Web Developers use it to create a skeleton of modern websites and web apps.
In simple words, HTML is the primary building block to create and structure website content.
HyperText
HyperText is a way of organizing text that allows the reader to easily navigate and access related information. It takes the reader to a different part of the same web page, or to a different web page altogether.
Markup Language
A markup language is a computer language that is used to add structure and formatting to a text document. Markup languages use a system of tags to define the structure and content of a document. These tags are interpreted by a program or application to display the document in a specific way.
Example of HTML
Let's see a simple example of HTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>programiz</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
<p>You'll learn about HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

HTML Basics
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
HTML Hierarchy
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of the content on the web page.
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render the web page. For example,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page. </p>
<p>
It contains a <strong>main heading </strong> and
<em> paragraph </em>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In this example, the html element is the root element of the hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body. The head element, in turn, contains a child element called the title, and the body element contains child elements: h1 and p.
Web Design Basics
Web design refers to the process of creating and styling the appearance of a website. There are 3 fundamental technologies to build the modern website and web applications. They are:
- HTML
- CSS
- JS
These technologies work together to provide the structure, style, and interactivity of a web page.
HTML
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links. Let's see an example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorials.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

Here, we have an HTML document where:
- <h1>— heading of the document
- <p>—paragraph of the document
The heading and paragraph tag in the above code help create a webpage structure.
CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language. It is used to style HTML documents.
It specifies how the elements of HTML look including their layout, colors, and fonts. We use <style> tag to add CSS to HTML documents. Let's add some CSS to our previous HTML code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorial.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In the above code, we've applied CSS to <h1> and <p> tags to change their text color. Notice the code,
h1 {
color: blue;
}
This CSS code turns the text color of every <h1> element into blue.
HTML Paragraphs
The HTML tag is used to create paragraphs. For example,
<p>HTML is fun to learn.</p>
Browser Output

As we can see, a paragraph starts with the <p> and ends with the </p> tag.
HTML Headings
The HTML heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) are used to add headings to a webpage. For example,
<h1>This is heading 1.</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2.</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3.</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4.</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5.</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6.</h6>
Browser Output

In the example, we have used tags h1 to h6 to create headings of varying sizes and importance.
The h1 tag denotes the most important heading on a webpage. Similarly, h6 denotes the least important heading.
The difference in sizes of heading tags comes from the browser's default styling. And, you can always change the styling of heading tags, including font size, using CSS.
HTML Inline and Block Elements
HTML elements can be broadly categorized into one of two categories:
- Inline Elements: <span>, <a>, <strong>, <img> etc.
- Block Elements: <p>, <div>, <h1>, <figure> etc.
HTML Inline Elements
Inline elements are displayed on the same line. They do not start on a new line and take up only as much width as their contents require. An example of an inline element is the <span> tag.
<p>This is how <span style="border: 1px solid black">span</span> works. </p>
Browser Output

HTML Links
HTML links or hyperlinks connect one resource on the web to another. The resource may be an image, a web page, a program, a video clip, an audio clip, an element within a web page, etc, or anything that can be hosted on the internet.
We use the HTML <a> tag to create hyperlinks. The syntax for the <a> tag is
<a href="URL"> Text </a>
Here,
- URL - the destination of the link
- Text - the part that will be visible as a link
Clicking on the text will navigate you to the resource in the URL. For example,
Browser Output

Here, clicking on the Swift Continue Statement will take you to
https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement.
Here,
max-width: 672pxswitches the layout from desktop to mobile when the viewport reaches a maximum width of672px.
flex-direction: columnvertically stacks the sidebar and main content on top of each other.
- Setting
widthto100%for both the sidebar and main content allows them to take up the full width of the document.
- Finally,
position: relativeallows the table of content to move with scroll, ensuring a good user experience for smaller mobile devices.
Note: For the desktop layout, the table of content (sidebar) and main content (.main-content) were positioned beside each other, while for the mobile layout, they are stacked vertically.
Complete Code of Documentation Page
Here is the final code of our HTML Documentation Page built in this tutorial.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>HTML Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- header element consisting of a logo and a heading -->
<header>
<div class="logo-wrapper">
<img
src="https://cdn.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/pc_logo.svg"
alt="Programiz Logo"
/>
</div>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
</header>
<main class="main">
<!-- a sidebar consisting of menu of documentation page -->
<aside class="table-of-content">
<h2 class="menu-heading">Table of Contents</h2>
<!-- main menu of table of content -->
<ul class="main-menu">
<li class="menu-sub-heading">Introduction</li>
<!-- submenu -->
<ul class="sub-menu">
<li><a href="#what-is-html">What is HTML?</a></li>
<li><a href="#html-basics">HTML Basics</a></li>
<li>
<a href="#web-design-basics">Web Design Basics</a>
</li>
</ul>
<li class="menu-sub-heading">HTML Basics</li>
<!-- submenu -->
<ul class="sub-menu">
<li>
<a href="#html-paragraphs">HTML Paragraphs</a>
</li>
<li><a href="#html-headings">HTML Headings</a></li>
</ul>
<li class="menu-sub-heading">HTML Inline</li>
<!-- submenu -->
<ul class="sub-menu">
<li>
<a href="#block-and-inline">Block and Inline</a>
</li>
<li><a href="#html-links">HTML Links</a></li>
</ul>
</ul>
</aside>
<!-- main content of documentation page will be here -->
<section class="main-content">
<h2 id="what-is-html">What is HTML?</h2>
<p>
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is used to structure and
format the content of websites on the World Wide Web. Web
Developers use it to create a skeleton of modern websites
and web apps.
</p>
<p>
In simple words, HTML is the primary building block to
create and structure website content.
</p>
<h3>HyperText</h3>
<p>
HyperText is a way of organizing text that allows the reader
to easily navigate and access related information. It takes
the reader to a different part of the same web page, or to a
different web page altogether.
</p>
<h3>Markup Language</h3>
<p>
A markup language is a computer language that is used to add
structure and formatting to a text document. Markup
languages use a system of tags to define the structure and
content of a document. These tags are interpreted by a
program or application to display the document in a specific
way.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2>Example of HTML</h2>
<p>Let's see a simple example of HTML.</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>programiz</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
<p>You'll learn about HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-example-on-browser.png"
alt="Browser Output"
/>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-basics">HTML Basics</h2>
<p>
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used
to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses
various tags to define the different elements on a page,
such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
</p>
<h3>HTML Hierarchy</h3>
<p>
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be
nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of
the content on the web page.
</p>
<p>
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document
Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render
the web page. For example,
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page. </p>
<p>
It contains a <strong>main heading </strong> and
<em> paragraph </em>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-basics-hierarchy.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<p>
In this example, the html element is the root element of the
hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body.
The head element, in turn, contains a child element called
the title, and the body element contains child elements: h1
and p.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="web-design-basics">Web Design Basics</h2>
<p>
Web design refers to the process of creating and styling the
appearance of a website. There are 3 fundamental
technologies to build the modern website and web
applications. They are:
</p>
<ul>
<li>HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>JS</li>
</ul>
<p>
These technologies work together to provide the structure,
style, and interactivity of a web page.
</p>
<h3>HTML</h3>
<p>
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used
to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses
various tags to define the different elements on a page,
such as headings, paragraphs, and links. Let's see an
example:
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorials.</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/web-design-basics-html-example.png"
alt="HTML example"
/>
<p>Here, we have an HTML document where:</p>
<ul>
<li>
<span><h1></span>— heading of the document
</li>
<li>
<span><p></span>—paragraph of the document
</li>
</ul>
<p>
The heading and paragraph tag in the above code help create
a webpage structure.
</p>
<h3>CSS</h3>
<p>
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language. It is
used to style HTML documents.
</p>
<p>
It specifies how the elements of HTML look including their
layout, colors, and fonts. We use <style> tag to add
CSS to HTML documents. Let's add some CSS to our previous
HTML code.
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorial.</p>
</body>
</html>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/web-design-basics-css-example.png"
alt="HTML example"
/>
<p>
In the above code, we've applied CSS to <h1> and
<p> tags to change their text color. Notice the code,
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
</code>
</pre>
<p>
This CSS code turns the text color of every <h1>
element into blue.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-paragraphs">HTML Paragraphs</h2>
<p>The HTML tag is used to create paragraphs. For example,</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code><p>HTML is fun to learn.</p></code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-paragraph.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<p>
As we can see, a paragraph starts with the <p> and
ends with the </p> tag.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-headings">HTML Headings</h2>
<p>
The HTML heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) are used to
add headings to a webpage. For example,
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<h1>This is heading 1.</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2.</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3.</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4.</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5.</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6.</h6>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/headings-in-html.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<p>
In the example, we have used tags h1 to h6 to create
headings of varying sizes and importance.
</p>
<p>
The h1 tag denotes the most important heading on a webpage.
Similarly, h6 denotes the least important heading.
</p>
<p>
The difference in sizes of heading tags comes from the
browser's default styling. And, you can always change the
styling of heading tags, including font size, using CSS.
</p>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="block-and-inline">HTML Inline and Block Elements</h2>
<p>
HTML elements can be broadly categorized into one of two
categories:
</p>
<ul>
<li>
Inline Elements: <span>, <a>,
<strong>, <img> etc.
</li>
<li>
Block Elements: <p>, <div>, <h1>,
<figure> etc.
</li>
</ul>
<h3>HTML Inline Elements</h3>
<p>
Inline elements are displayed on the same line. They do not
start on a new line and take up only as much width as their
contents require. An example of an inline element is the
<span> tag.
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<p>This is how <span style="border: 1px solid black">span</span> works. </p>
</code>
</pre>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-inline-example.png"
alt="HTML Example"
/>
<hr class="section-break" />
<h2 id="html-links">HTML Links</h2>
<p>
HTML links or hyperlinks connect one resource on the web to
another. The resource may be an image, a web page, a
program, a video clip, an audio clip, an element within a
web page, etc, or anything that can be hosted on the
internet.
</p>
<p>
We use the HTML <a> tag to create hyperlinks. The
syntax for the <a> tag is
</p>
<pre class="code-block">
<code>
<a href="URL"> Text </a>
</code>
</pre>
<p>Here,</p>
<ul>
<li>URL - the destination of the link</li>
<li>Text - the part that will be visible as a link</li>
</ul>
<p>
Clicking on the text will navigate you to the resource in
the URL. For example,
</p>
<h3>Browser Output</h3>
<img
src="https://www.programiz.com/sites/tutorial2program/files/html-link-example.png"
alt="HTML example"
/>
<p>
Here, clicking on the Swift Continue Statement will take you
to
</p>
<p>
<a
href="https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement"
>https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement.</a
>
</p>
</section>
</main>
<footer>
<p>HTML Documentation Page © Programiz, 2023</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>/* resets the browser default spacing */
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
width: 100%;
max-width: 760px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* styles the header element */
header {
height: 80px;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
background-color: aliceblue;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 4px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.116);
}
/* styles for logo wrapper*/
header .logo-wrapper {
width: 100px;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 20px;
transform: translateY(-50%);
cursor: pointer;
}
/* styles to fit logo image within the logo wrapper */
.logo-wrapper img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
object-fit: cover;
}
/* style for the main heading of page */
header h1 {
line-height: 80px;
color: #25265e;
}
.table-of-content {
/* remaining width for the main content of page */
width: 30%;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.137);
color: #25265e;
padding: 8px;
height: 450px;
/* makes the sidebar sticky */
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}
.menu-heading {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.table-of-content ul {
/* removes the bullet points in list items */
list-style-type: none;
/* list item marker is placed within the content area of the list item */
list-style-position: inside;
padding-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
/* styles for sub-heading inside our menu */
.menu-sub-heading {
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: none;
margin-bottom: 12px;
color: #25265e;
}
/* provides the bottom spacing for each list item in menu */
.sub-menu li {
margin-bottom: 16px;
}
/* color the menu item */
.table-of-content a {
color: #25265e;
}
/* change color of menu items while on hovering */
.table-of-content a:hover {
color: blue;
}
/* changes color while menu items are clicked */
.table-of-content a:active {
color: red;
}
.main {
/* default width is always 100% */
width: 100%;
/* aligns the sidebar and main content horizontally next to each other */
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
gap: 20px;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 4px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.116);
}
/* styes for the main content */
.main-content {
/* sets 70% width of the document, 25% is occupied by sidebar earlier,
and remaining for spacing between them */
width: 70%;
padding: 10px;
}
h2,
h3 {
color: #25265e;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
p {
margin-bottom: 24px;
line-height: 24px;
}
/* styles the under ordered list in main element */
.main ul {
list-style-position: inside;
padding-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
/* adds margin to top and botton for hr element for spacing */
.section-break {
margin: 24px 0px;
}
/* styles the code block */
pre.code-block {
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.13);
background-color: aliceblue;
margin-bottom: 24px;
white-space: pre-line;
}
/* images are allowed to shrink for smaller screen sizes */
.main-content img {
max-width: 100%;
}
/* style for footer */
footer {
height: 50px;
font-size: 14px;
text-align: center;
color: #25265e;
background-color: aliceblue;
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.26);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 4px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.116);
}
/* provide line-height same as height of footer to vertically center */
footer p {
line-height: 50px;
}
/* adding media query for responsiveness */
@media screen and (max-width: 672px) {
/* the sidebar and content are stacked on top of each other */
.main {
flex-direction: column;
}
/* takes the full width of the document */
.table-of-content {
width: 100%;
position: relative;
}
/* takes the full width of document */
.main-content {
width: 100%;
}
}Browser Output

HTML Tutorial
Table of Contents
What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is used to structure and format the content of websites on the World Wide Web. Web Developers use it to create a skeleton of modern websites and web apps.
In simple words, HTML is the primary building block to create and structure website content.
HyperText
HyperText is a way of organizing text that allows the reader to easily navigate and access related information. It takes the reader to a different part of the same web page, or to a different web page altogether.
Markup Language
A markup language is a computer language that is used to add structure and formatting to a text document. Markup languages use a system of tags to define the structure and content of a document. These tags are interpreted by a program or application to display the document in a specific way.
Example of HTML
Let's see a simple example of HTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>programiz</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
<p>You'll learn about HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

HTML Basics
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
HTML Hierarchy
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of the content on the web page.
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render the web page. For example,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page. </p>
<p>
It contains a <strong>main heading </strong> and
<em> paragraph </em>.
</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In this example, the html element is the root element of the hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body. The head element, in turn, contains a child element called the title, and the body element contains child elements: h1 and p.
Web Design Basics
Web design refers to the process of creating and styling the appearance of a website. There are 3 fundamental technologies to build the modern website and web applications. They are:
- HTML
- CSS
- JS
These technologies work together to provide the structure, style, and interactivity of a web page.
HTML
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links. Let's see an example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorials.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

Here, we have an HTML document where:
- <h1>— heading of the document
- <p>—paragraph of the document
The heading and paragraph tag in the above code help create a webpage structure.
CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language. It is used to style HTML documents.
It specifies how the elements of HTML look including their layout, colors, and fonts. We use <style> tag to add CSS to HTML documents. Let's add some CSS to our previous HTML code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Programiz</h1>
<p>We create easy to understand programming tutorial.</p>
</body>
</html>
Browser Output

In the above code, we've applied CSS to <h1> and <p> tags to change their text color. Notice the code,
h1 {
color: blue;
}
This CSS code turns the text color of every <h1> element into blue.
HTML Paragraphs
The HTML tag is used to create paragraphs. For example,
<p>HTML is fun to learn.</p>
Browser Output

As we can see, a paragraph starts with the <p> and ends with the </p> tag.
HTML Headings
The HTML heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) are used to add headings to a webpage. For example,
<h1>This is heading 1.</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2.</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3.</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4.</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5.</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6.</h6>
Browser Output

In the example, we have used tags h1 to h6 to create headings of varying sizes and importance.
The h1 tag denotes the most important heading on a webpage. Similarly, h6 denotes the least important heading.
The difference in sizes of heading tags comes from the browser's default styling. And, you can always change the styling of heading tags, including font size, using CSS.
HTML Inline and Block Elements
HTML elements can be broadly categorized into one of two categories:
- Inline Elements: <span>, <a>, <strong>, <img> etc.
- Block Elements: <p>, <div>, <h1>, <figure> etc.
HTML Inline Elements
Inline elements are displayed on the same line. They do not start on a new line and take up only as much width as their contents require. An example of an inline element is the <span> tag.
<p>This is how <span style="border: 1px solid black">span</span> works. </p>
Browser Output

HTML Links
HTML links or hyperlinks connect one resource on the web to another. The resource may be an image, a web page, a program, a video clip, an audio clip, an element within a web page, etc, or anything that can be hosted on the internet.
We use the HTML <a> tag to create hyperlinks. The syntax for the <a> tag is
<a href="URL"> Text </a>
Here,
- URL - the destination of the link
- Text - the part that will be visible as a link
Clicking on the text will navigate you to the resource in the URL. For example,
Browser Output

Here, clicking on the Swift Continue Statement will take you to
https://www.programiz.com/swift-programming/continue-statement.